Generators are amazing machines. They create the power we use to turn on lights, run appliances, and keep our homes and businesses going. But did you know that one of the most important things about a generator is its frequency? If the frequency isn’t right, all sorts of problems can happen. In this article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about the frequency of a generator, in a way anyone—even a 10-year-old—can understand.
What Does Frequency of a Generator Mean?
The frequency of a generator tells us how fast the electricity is cycling, or switching back and forth. In the United States, this is usually 60 Hertz (Hz). That means the electricity changes direction 60 times per second.
Imagine a swing going back and forth. The number of times it swings in a second is like the frequency. When a generator works, it spins and creates electricity. The speed of that spinning affects the frequency.
In technical terms, frequency is how many times an alternating current (AC) wave completes a full cycle in one second. One cycle = one wave going up and down. So if a generator is producing 60Hz, it’s sending out 60 of these waves each second.
The engine speed of the generator (measured in RPM – revolutions per minute) is connected to the frequency. A small change in RPM can cause the frequency to change too. That’s why keeping the engine speed steady is super important.
Why Is Generator Frequency So Important?
The frequency of a generator might sound like a small detail, but it affects everything that runs on electricity. Every appliance, light, motor, and device in your home is designed to run on a specific frequency—usually 60Hz in the U.S. or 50Hz in some other countries.
If the frequency is too low, things slow down or don’t work right. If it’s too high, things can burn out or break.
Here’s why it matters:
- Appliances work best at a stable frequency. Your microwave, fridge, or TV might stop working if the frequency isn’t stable.
- Motors depend on frequency. Tools and machines with electric motors (like air conditioners, compressors, and fans) need the right frequency to spin at the correct speed.
- Lights and electronics can flicker or behave strangely.
- Power grids require a synchronized frequency. Large generators feeding power into a grid must match the grid’s frequency perfectly.
What Happens If the Frequency Changes Too Much?
If the frequency of your generator goes too high or too low, it can cause serious problems. That’s why keeping the frequency close to 60Hz is so important.
Lights Can Flicker or Go Out
Lights are sensitive to frequency. If the frequency is too low, your lights may dim or flicker. If it drops too far, they might shut off completely. High frequency can cause some LED or fluorescent lights to buzz or flicker, too.
Machines Can Break
Motors in machines—like washing machines, compressors, or tools—rely on a stable frequency. If the frequency goes off, they might run too fast or too slow. That puts stress on the motor and can lead to overheating, burnout, or mechanical failure.
Power Can Go Out
A generator running at the wrong frequency might shut down to protect itself or connected devices. If it’s part of a larger system (like in a hospital or business), incorrect frequency can cause total power failure, which could be dangerous or costly.
How Do Generators Keep the Right Frequency?
Good question! Generators have systems that help them keep the frequency stable. The most important part is the governor. A governor controls the speed of the engine. If the engine tries to go faster or slower, the governor adjusts the fuel to keep it steady.
There are two types of governors:
- Mechanical governors – Use springs and gears to balance the engine speed.
- Electronic governors – Use sensors and control circuits to manage speed more precisely.
Modern generators often use inverter technology, which changes the engine power into very smooth and stable electricity. These are called inverter generators. They’re great at keeping the frequency and voltage stable, even when your power needs go up or down.
What Causes Frequency Problems in Generators?
Several things can make the frequency of a generator go out of range. Let’s look at the most common causes:
- Overloading the generator: If you plug in too many devices, the engine might slow down, which causes the frequency to drop.
- Sudden load changes: Turning on a big machine or appliance can pull power fast and cause a dip in frequency.
- Poor engine maintenance: Dirty air filters, old spark plugs, or bad fuel can make the engine run unevenly.
- Bad governor: If the governor doesn’t respond correctly, the engine speed can fluctuate, changing the frequency.
- Low fuel or poor-quality fuel: The engine may not run smoothly, especially if the fuel is old or mixed with water.
Knowing the cause of the problem is the first step in fixing it. That’s why checking the frequency regularly is important.
How to Check the Frequency of a Generator
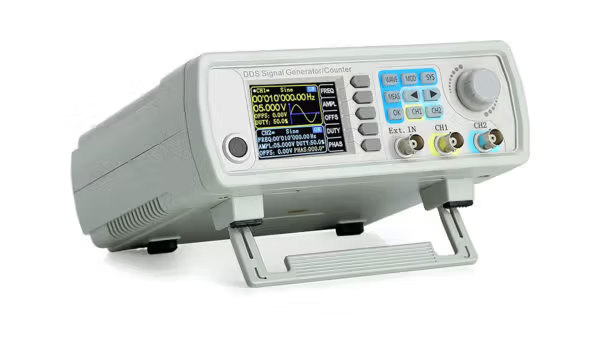
You can’t see frequency with your eyes, but there are a few easy ways to measure it. Here’s how you can check the frequency of your generator:
Use a Digital Meter
Many digital multimeters (DMMs) can check frequency. Plug the meter into a generator outlet (following safety steps), and switch to the Hz setting. This will show you the live frequency. Look for a reading close to 60.0 Hz. If it says 58 or 62, you might have a problem.
Try a Generator Monitoring App
Some newer generators connect to your phone using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. These smart generators come with an app that shows voltage, frequency, power usage, and more. If your generator supports this, it’s a super easy way to check the frequency anytime.
Look at the Generator Display
Some portable and standby generators come with a built-in LCD or LED screen. This display often shows the frequency (Hz), voltage (V), and other data. Just check the screen and look for the frequency value.
Can You Fix Frequency Problems Yourself?
Sometimes yes, but not always. If the problem is simple—like overloading the generator—you can unplug some devices, let the engine stabilize, and see if the frequency goes back to normal.
You can also clean the air filter, check the spark plug, and make sure your fuel is fresh. These steps can help the engine run more smoothly and keep the frequency steady.
But if the problem is inside the governor or alternator, or if the frequency is jumping around even with no load, it’s better to call a generator technician. Fixing frequency issues often requires tools and knowledge that most people don’t have at home.
The Bottom Line
The frequency of a generator is one of the most important parts of how it works. In the United States, that means your generator needs to produce a steady 60Hz. If the frequency goes up or down, your lights can flicker, your machines might break, and your power could go out.
Keeping the frequency right means:
- Using the right amount of power (not overloading).
- Maintaining your generator properly.
- Checking frequency with a meter, display, or app.
Now that you understand generator frequency, you can use your generator more safely and efficiently. And remember—whether you’re powering your house, an RV, or a work site, a steady 60Hz means everything runs smoothly.

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months ago
 Life Style8 months ago
Life Style8 months ago
 Life Style7 months ago
Life Style7 months ago
 Games7 months ago
Games7 months ago
 Life Style8 months ago
Life Style8 months ago
 Life Style7 months ago
Life Style7 months ago
 Education8 months ago
Education8 months ago
 Life Style7 months ago
Life Style7 months ago






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Oscar-Mayer-Bacon-Recall-FT-BLOG0725-5487d56caf754cff912e871fc609878f.jpg)






